Catalog
Uncontrolled thermal energy will shorten the life
of a component or kill it altogether. Thermal management is becoming
increasingly necessary for electronic systems to maintain operational
reliability. People use heat sinks to meet these goals. A heat sink is a heated
dissipative device with a base and fins extending outward. In this article, you
can determine which one you should purchase after reading about the various
features and types of heat sinks.
Heat Sink Material
Aluminum Heat Sinks
Aluminum is lighter with the ability to carry
heat energy dramatically, which is an ideal choice for aluminum extrusions heat
sinks. Studies have shown that the thermal conductivity of aluminum is 167
W/m.K compared to 50 W/m.K for steel, indicating that aluminum has a higher
thermal conductivity—3 times that of steel. In addition, aluminum heat sink has
more surface finish options than copper, such as anodizing, hot-dip
galvanizing, painting, sandblasting, etc. Most heat sinks can be widely used
for large machinery for their cheap price. At present, it is widely used in
SSR, inverter, SVG, power supply, etc.
Copper Heat Sinks
Compared to aluminum, copper heat sinks have a
better heat dissipation ability than aluminum with a thermal conductivity of
401 W/m.K – much excel than thermal performance of aluminum. However, copper is
3 times heavier and more expensive than aluminum. Therefore, for processors to
purchase copper radiators is a very costly approach as aluminum can be surface
treated to achieve similar performance to copper. Therefore, copper heat sinks
are generally installed in server mainframes, computer heat sink, and
automotive air conditioners. Due to its chemical inactivity, copper doesn’t
make surface treated unless there are other special requirements.
Heat Sink Working Method
Active Heat Sinks
Known as “active heat sinks”, heat sinks assemblies are used in conjunction with cooling fans, which is the most common form of heat conduction. Active heat sinks depends on fans to rotate the surrounding air flow between the fins, so thermal dissipation will be more efficient, which means active heat sink can be designed in small sizes to meet different demands. In addition to the classic cooling method, water as a cooling medium is also an alternative and sound approach to dissipate heat, but maybe you will spend additional money.
Passive Heat Sinks
Passive heat exchanger is one of the heat sink
types that I will mention below. Known as “passive heat sinks”, they
are not equipped with any auxiliary devices to reduce components’ temperature
whereas heat sink transfers heat generated from working parts. Considered an
individual solution for thermal management, it is usually physically larger
than the active heat sink. passive heat sink provides them with a larger
surface area due to being machined into the typical finned heat sink structure.
Heat Sink Types and Manufacturing Process
Categorized by deformation process——
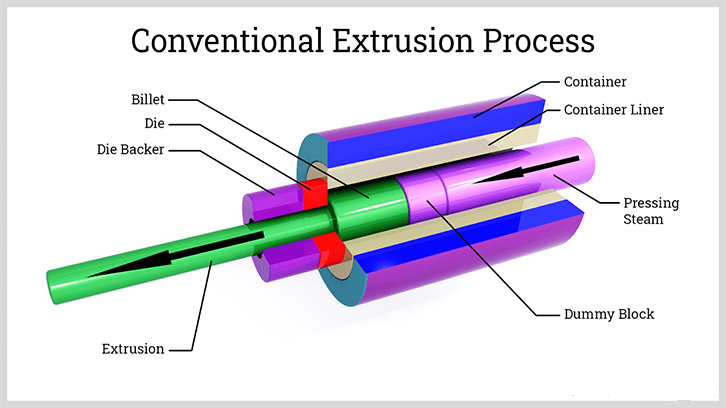
Extruded Heat Sinks
Basically, nearly all heat sinks are produced by extrusion and listed as passive heat sinks. This is a typical metal-forming process in which heated aluminum strips are forced through a die with a specific cross-sectional area to extrude long strips and then form a uniform-sized heatsink. After that, the operator will cut it into different sizes according to customer requirements.
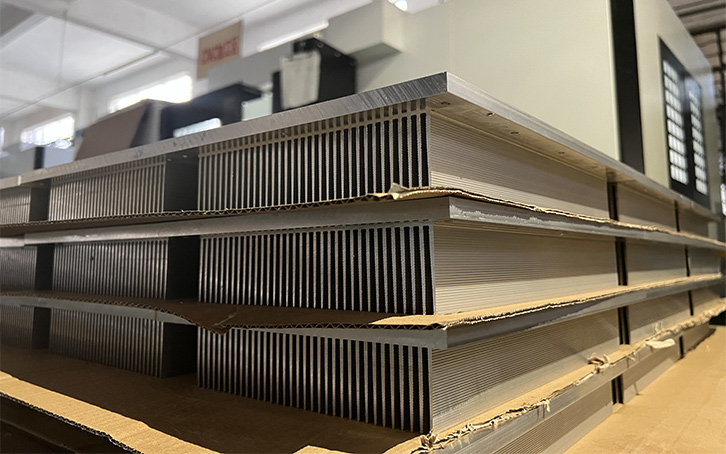

Currently, there are two main extrusion methods: hot heading and cold heading. Hot heading is the extrusion of blanks heated to 25°C below the melting temperature, while cold heading is high plasticity and low hardness at room temperature. The former is widely used in construction machinery or heat sink groups for traffic engineering. On the contrary, cold heading can produce small durable parts such as nuts, bolts, etc. Currently, it is recommended that aluminum is the most cost-effective material for extrusion heat sink with great thermal resistance. But you should consider what aluminum alloy you should choose as there are 6 aluminum types with discrepant features.
Advantages
1, Easy to produce complex cross-sections: Due to the minimal error in the extrsion, different types of extruded heat sinks can be manufactured without any effort with low costs.
2, Ability to form brittle material: As aluminum is a plastic metal, the extruded heat sink doesn’t generate any cracks.
3, Hollow parts: The shaft can be made into hollow parts through the interplay of the die and axis
4, Flexibility in operation: Only fine adjustments to process parameters are required to change the specifications of extruded heatsink in a timely manner—— without interruption in the production process.
5, Surface Finish: The heat sink’s surface can be buffed or polished to achieve a mirror-like surface or brushed for a matte finish.
Disadvantages
1, Costs for Die Maintenance: Long-time use will affect the accuracy of the product as well as its working life for which extrusion will generate a lot of pressure
2, Costs for Tooling Customization: Producing extruded heatsinks with special shapes requires custom and proprietary tooling, which will cost an additional budget. Therefore, it is better to produce large quantities to apportion the tooling cost.
3, Production Time: Although the machine can extrude a large number of heatsinks at one time, it takes longer for avoiding deformation.
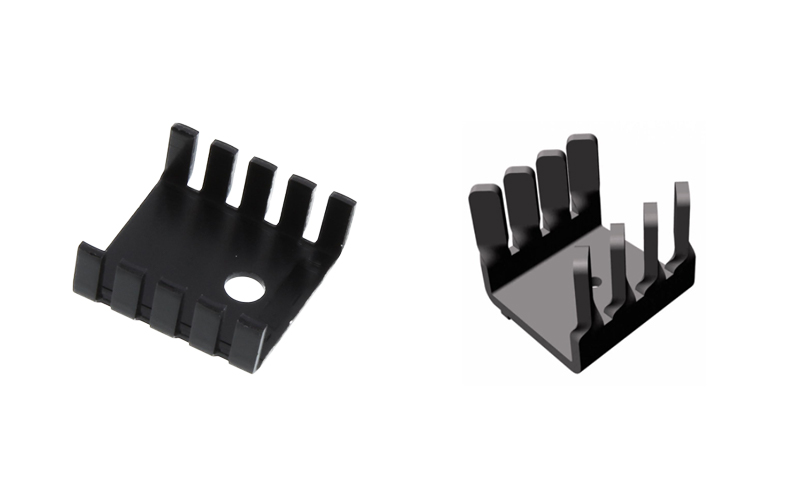
Stamped Heat Sinks
Stamping is a cost effective solution. So are
heatsinks. These heat sinks are made by a progressive stamping process, where
the heat sink develops more details and features with the number of dies it
passes through. These heat sinks are mainly made of stamped materials such as
copper, aluminum, steel plates, etc. The common sizes are 40x40mm, 50x50mm,
etc. They are mainly used in small electronic packages such as cell phones,
tablets, smartwatches, etc. Due to their small size, stamped heat sinks come
with surface treatments to speed up air velocity and thermal radiation to
reduce ambient temperature.

Advantages
1,
Cost: Low cost to meet the mass production and simple mold construction types
of heat sinks
2,
Quality: Thanks to the progressive press, it is possible to quickly produce
stamped radiators with intricate details and ensure that the specifications are
consistent from one radiator to the next.
3,
Surface Treatment: Parts with surface treatment significantly improve
durability
Disadvantages
1,
Volume: Because of the small size of the stamped heat sink, so not suitable for
large electronic packaging
2,
Performance: Stamped heat spreader is limited by its shape, performance can
only dissipate thermal energy in the range of small appliances
Bonded Fin Heat Sink
It
is an alternative to the spade tooth heat sink. This bonded design is mainly
used for manufacturing large-size heat sinks for automotive, consumer
electronics, UPS, and industrial control applications. Hest sink consists of a
number of fins and a base, where the fins are cut from aluminum blanks while
the base can be molded by die-casting. Afterward, the two are joined together
by epoxy, brazing, or soldering.
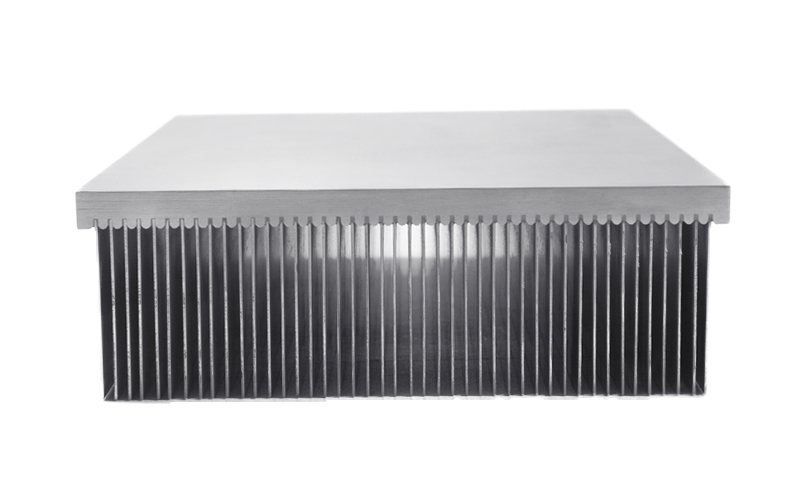

Advantages
1, Customization: Allows for custom fin density and mass ratio, representing better heat dissipation than extruded heat sink. In addition, the material, pattern, finish, and shape of the fins can be customized to meet specific needs.
2, Cost: Because the manufacturing does not involve complex processes, the production cost of heat sink is lower ( but slightly more expensive than finned heat sinks with the same specifications)
Disadvantages
1,
Strength: Since the whole structure is only fixed by adhesive, it is easy to
twist or decompose under special conditions such as high temperature or low pressure.
2,
Appearance: Since it is manually spliced, the weld is slightly rough which
affects the overall aesthetics.
3,
Corrosion Resistance: Due to utilizing a large amount of adhesive, it is not
strong against acid and alkali corrosion.
Forged Heat Sinks
Manufacturing
forged heat sink requires a large casting machine (3500-5000T). The operator
adjusts the set parameters and places the aluminum block into the machine,
while it is a handy operation that the punch inside the machine pushes the
block upwards to generate heat sink design. Currently, the most common forged
heat sinks are round and a few squares. Heat sink is mainly used for LED
lighting, circuit modules, and monitors.
Advantages
1,
Size: Small size and suitable for small and medium-sized electronic devices
popular in the market.
2,
Process: Due to the simple production, it can be mass-produced
Disadvantages
1, Weight: Due to the special fin shape, the forged heat sink will seem heavier in the same size radiator (especially if the diameter is above 5 inches).
2, Design: Most shapes are round and square, offering limited heat sink design
3, performance: Continuous air flow is not as good as extruded heat sink, resulting in slower heat transfer.
Die Casting Heat Sinks
It
is key to require a large die casting machine for manufacturing die casting
heat sinks. The process involves placing casting material into the mold shell,
where its shape will be changed under high pressure to produce heat sinks with
varied sizes such as round, hexagonal, and square. After that, the finished
product is polished to remove the edges for surface treatment. At present,
mainstream die-casting heatsinks are used for large equipment such as
transformers, new energy vehicle battery pallets, etc.
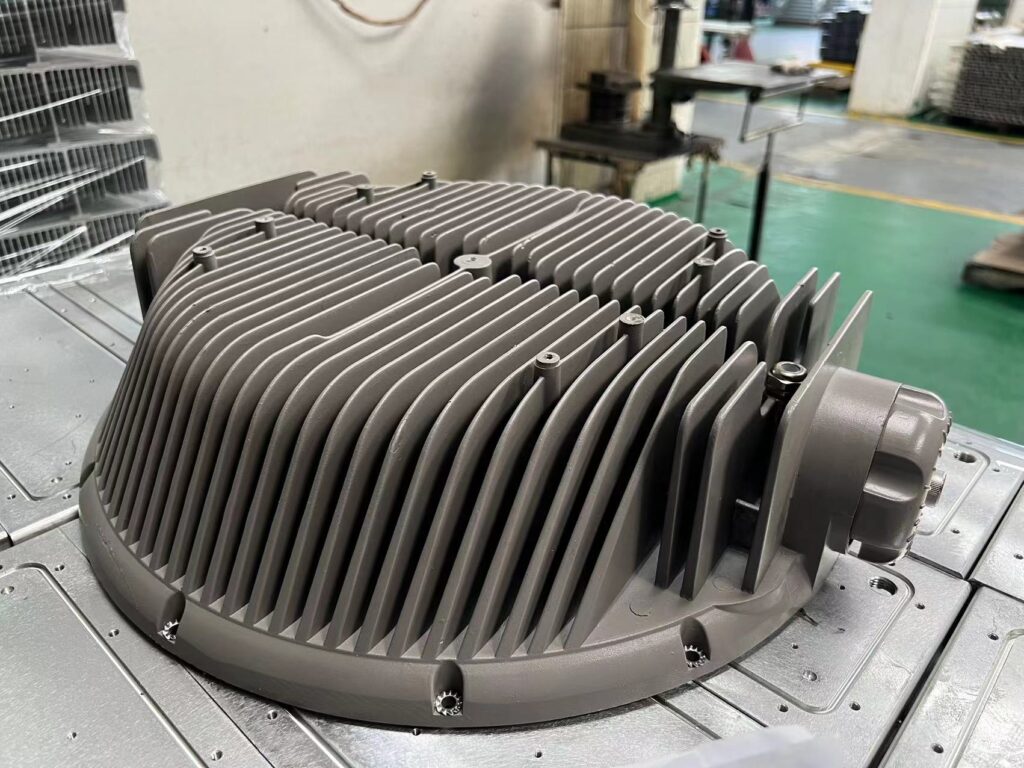

Advantages
1,
Quality: Castings are highly accurate and gift excellent durability, suitable
for manufacturing complex parts
2,
Production Efficiency: Die casting machine realizes automatic operation, thus
greatly improving the production speed
3,
Cost: It saves a lot of costs cause that die-casting can achieve rapid mass
production while improving the utilization of metal
4,
Appearance: Ability to design into different shapes to meet the aesthetic
requirements of different people.
Disadvantages
1, Process: Due to the short die casting time, metal with high melting point such as copper, ferrous metal, etc. will generate pores affecting the product life. Therefore, it is recommended to adopt low melting point metals such as aluminum
2, Mold Price: It is expensive for customized mold, hence small batch production is not a cost-effective solution
Folded Fin Heat Sink
This
fin heat sink is designed for high-power, forced convection applications where
space is limited, such as heat sinks inside ventilation ducts. It uses internal
fins or multiple external fins to expand the surface area to dissipate thermal
energy, reducing up to 60% heat flow. Folded fin heat sinks consist of a metal
sheet that is folded and later welded to the base of the heat sink in a way
that does epoxy resin or brazing.

Advantages
1, Performance: Due to the special structure, it can effectively reduce the ambient air temperature
2, Customization: In addition to aluminum, fins can also be selected from copper, stainless steel, nickel alloy, or other metals, but the price is more expensive than aluminum; in addition, the shape of the fins can be changed at will. Currently, wave-shaped and ruffled heat sink has been leading a trend.
3, Weight: Much lighter than extruded heatsinks
Disadvantages
1,
Quality: As the base and fins have to be welded together, they are likely to
fall off over time, especially when using epoxy resin
2,
Cost: Much more expensive than the extrusion heat sink
3,
Installation: Installation will be more troublesome in the restricted space
Categorized by cutting process——
CNC Machined Heat Sinks
Unlike deformation, CNC machining is one of the mainstream manufacturing processes that can produce different sizes of heat sinks. CNC machining is usually used in conjunction with extrusion to produce the basic shape, and then CNC machining is used to create complex faces, slots, and holes for heat sink. Alternatively, aluminum blocks can be cut into specific shapes with CNC lathes, but this is more costly.
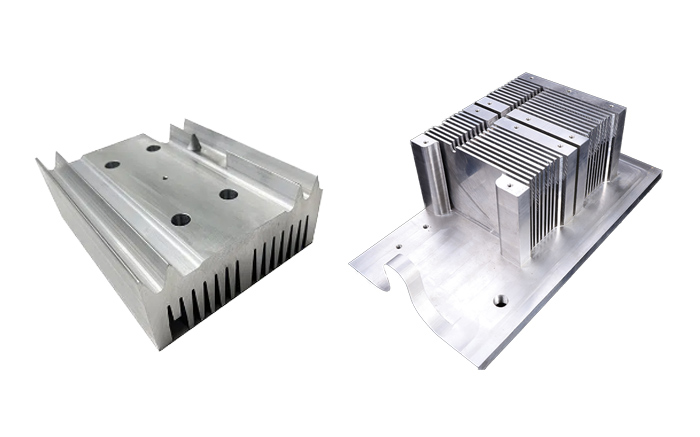

Advantages
1, High Degree of Customization: No matter what shape and specifications, CNC machining can make that happen
2, Processing Accuracy: Obtain the same specifications without any errors
Disadvantages
1, Cost: Due to high quality and performance, the cost of CNC machining is more expensive compared to other heat sink types.
2, Production Time: Due to the complex CNC machining, it will cost much time to manufacture
Skiving Heat Sink
Since heat sink performance is related to the quantity and shape of fins. Therefore, it is indispensable to combine several fins into a single unit to improve its performance, which is why skiving heat sinks are so popular today. They are mainly used in power plants for high-power equipment such as photovoltaic inverters, wind power converters, power packs for new energy automobiles, etc.
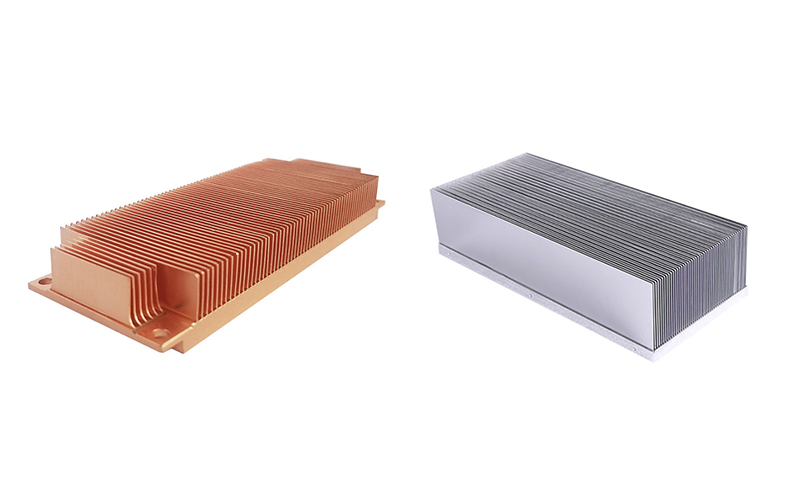
To make finned heat sinks, a large shovel tooth machine is required. It uses a unique “V” shaped tool that scrapes the fins from the surface and then bends the fins into a vertical position while leaving a curved interface at the bottom. After machining, the operator performs subsequent processing such as deburring and tapping after cutting fins to a specified size. Indeed, slotting, tube pressing, epoxy welding, etc. can be done as any special requirement.
Advantages
1, Raw Material: Made from aluminum blanks without additional processing, meaning no raw material loss during production
2, Cost: moderate Price with good performance, it is recommended to apportion cost of each heat sink through mass production
Disadvantages
1, Weight: Heavy, not suitable for light machinery
2, Hardness: Thin fins indicate there is a possibility that the deformation of fins will have an effect to transfer heat
3, Thermal Conductivity: Thermal conductivity is mainly determined by the raw materials and structure, which means it can not be used with SSR, heat pipes, and other materials with ultra-high thermal conductivity
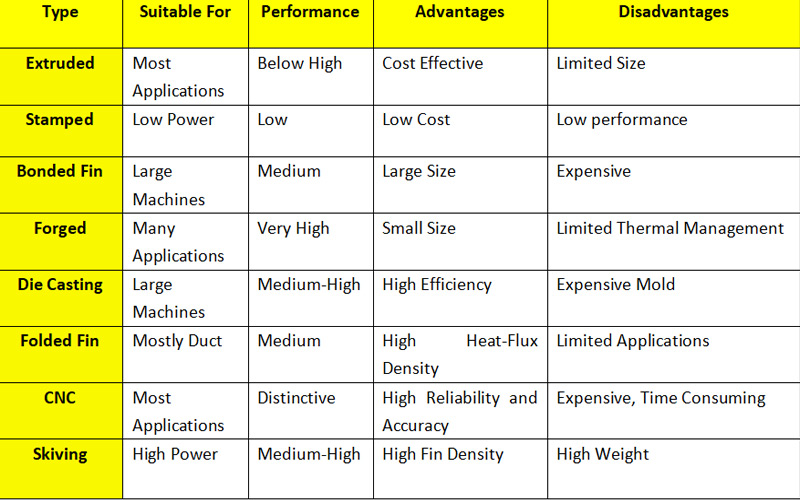
Conslusion
For easy to get point of view, the following is a reference for functions and applications between discrepant heatsinks: