There are advantages to CNC machining. Compared to manual machining, CNC processing technology has higher accuracy and processing efficiency while it also saves labor costs for using computers. However, if the machine is not properly maintained, it will directly affect surface quality. Here is a blog to learn about the common problems that can occur with CNC machining and ways to solve that issues.
Issues Happened in CNC Machining Process
Hydraulic System–
Mechanical Vibration
Every generation of CNC machines uses a chuck to clamp the workpiece. Since there is a small gap between the milling cutter and the chuck, the workpiece may vibrate during machining and thus affect the machining accuracy as the process is not completed with powerful force. In this circumstance, the amplitude of the end mill should be minimized to less than 0.02mm to ensure the CNC machining process well-performance.

With the development of hydraulic chucks, high production speed represents the hydraulic system can close and open the hydraulic chucks promptly. But components may be lost once any errors happened in the hydraulic machine, even though the reliability is greatly improved. Generally speaking, you can use a data collector to solve this problem.
Liquid leakage
The hydraulic system is consist of a transmission system, gap elimination device, and worm gear clamping device used to manufacture uniform specifications of CNC workpiece through a recycling operation. Due to improper use or lack of maintenance, several issues will occur such as liquid leakage, and serious damage to clean pipes, pumps, and regulator valves all of which will lead to low-efficiency operation.
More seriously, it will cause periodic occlusion hindering hydraulic control at any time because of high oil temperature or improperly assembled internal parts.
Fail to Synchronize
Given that servo motors maintain speed of the internal CNC machine tool. Regarding some large machined parts such as aluminum frames for trains, heatsinks for large machines, and housing structures for automobiles and electronic products, large volume, weight, and thickness will cause a plummet in the speed of the servo motor and off-sync in the transmission system during operations. Especially for CNC machine tools such as milling cutter rotors, it will be out of synchronization with the spindle speed, which will impact the precision of the machine parts.
Parts Jamming
The well-functioning hydraulic system counts on the hydraulic oil milling machine working in a clean environment. With several damping orifices and throttle clearance, control values and working pipelines are categorized as high-precision components. Increasing friction coefficient will intensify the friction and wear of the parts when contaminants get into them. Apart from that, clogging and jamming of parts will happen for big pollutants. This phenomenon is mainly attributed to several factors:
1, Contamination of the oil-filling tool
2, Solid impurities mixed in the oil
3, Oil mixed with air and water
4, Debris generated by excessive friction of the working parts
5, Lack of maintenance of working parts
Machine Overheating
Excessive speed and high temperature of the cutting tool will produce thermal stress on the cutting machine tool to deform the cutting material. In addition, the working environment at high temperatures causes a higher oil temperature, which not only affects the working life of the machine but also damages CNC machine tools, drills, and rubber gaskets. Typically, the life of hydraulic oil at 55°C is reduced by 50% for every 10°C increase.
CNC Machine Tool for Cutting Processes–
CNC Machine Tool Detachment
Most of the end mills in CNC machines are firmly fixed with a spring clamp. Since the blade is mounted in a cantilevered condition, the end mill may gradually protrude from the holder until it falls out during the milling process, which will lead to the scrapped materials.

Generally speaking, due to water-soluble cutting oil between the tool holder and the end mill shank, it can cause insufficient clamping and cutting force on the machine tool. Therefore, new end mills are coated with anti-rust oil. And CNC operators should clean and dry the oil inside the shank and tool holder before the installation of the end mill.
Tool Diameter and Positioning
The diameter of the milling tool is determined by the width of the workpiece and the power of the CNC machine. To avoid tears when using a machine tool, for example, we select suitable widths of the tool according to the surface area of the workpiece and adjust the feed rate to ensure good chip formation.
Tool Tear
Tool tear is caused by cutting with rapid speed or low processing performance. The solution is to reduce the speed of cutting – generally below 1 mm/min and not exceeding 6mm /min. Secondly, increasing the amount of tool travel is a way to extend working life for debilitating the cutting speed. Thirdly, replacing the tool materials, such as titanium, PCBN, ceramic, diamond, etc. However, due to the high cost of raw stuff with excellent Mohs hardness, you can also choose the electroplating process to enhance the hardness of the milling cutter, such as titanium nitride, titanium carbon nitride, or aluminum oxide.
Tool Breakage
There are many reasons for a broken blade, such as the low hardness of the shank, faster or lower cutting speed, high surface temperature, or a metal workpiece with higher hardness than the tool. In this case, the integrity of the blade and screws holding the blade in place should be checked to ensure a great performance. Finally, increasing the cutting speed to determine if the blade is fragile or any issues related to production quality.
Chip Accumulation (BUE)
Chip accumulation is a phenomenon that cumulative debris is stuck to the blade that cannot be removed.

With the accumulation of debris, several accidents will occur such as blade shattering, workpiece breakage, all of which affect production efficiency because of blade passivation, low CNC processing speed, and inability to remove chips. To solve this problem, we suggest you adopt the following methods:
1, Using a plating-coated milling cutter
2, Increasing the amount of tool travel
3, Equipping with coolant liquid
4, Using smooth milling
5, Adopting mineral oil such as crude oil, kerosene, etc.
6, Accessing the speed during CNC machining processing
Lubricating Oil
Check your CNC machining instruction manual for suitable lubricant, which ensures that your machine will operate well performance for a long time. Also, the fitting lubricant will maximize the working performance of your CNC machines, especially the spindle. Also, a end mill equipped with suitable cutting oil can cut specific metals:
1, Non-ferrous metals such as copper and aluminum: Given the low hardness, you can choose cutting oil with low anti-wear agent content with sound corrosion resistance.
2, Cast iron, and bronze with high brittleness: As cutting will produce a lot of debris to cause damage to the CNC machine tool, it is recommended to choose the lubricant with a better cleaning performance and remember to filter impurities.
3,Titanium alloys with high hardness:A comprehensive evaluation on the fluidity and corrosion resistance of the lubricant is required to prevent hydrogen embrittlement and chip accumulation during CNC manufacturing.
Notices in CNC Machining Processes
Tool Entry and Exit Conditions
The end mill will be affected by the “Impact Load” when entering into the cutout, stating that the cutout size is crucial between the end mill and the workpiece and so do the well-positioning end mill:
1, The workpiece width is larger than the end mill diameter: The blade cuts into the part while generating a huge impact from the machined part surface, which is called “Impulsive Load”; the blade is out of cutter but to keeps the tip contacting with other parts where cutting forces will be applied to the blade until it leaves the workpiece, which is called “Unloading Force”.
2, The workpiece width is smaller than the end mill diameter:
The blade bears accumulative Impulsie Load when entering or exiting the machining part, forcing the tool out of the machining workpieces.
Down or Up Milling
The direction of machined workpiece is different. The former is that the blade contacts the equipment surface from above and vice versa. It features different advantages:
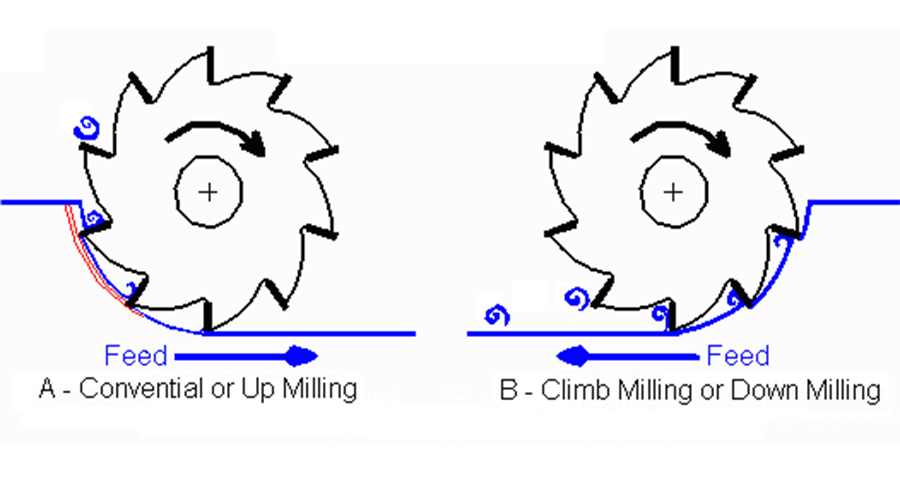
Down Milling
1, Less heat generated by milling
2, Preventing blade form deformation
Up milling
1, Small impact on the blade
2, Reducing the vibration of the spindle
Machining Processing Time
Long periods in manufacturing will lead to additional costs for the multiple uses of CNC machining tool, but the accuracy will be greatly improved; Keep in mind that product may be damaged as you have spent too much time in machine processing.

To meet your technical requirements, it is recommended that you look for a Chinese manufacturer with rich experience in CNC machining industries who can meet your machining requirements and provide various options for customization as well as explain how to reduce the cost of your product for you. If you are confounded, you can also contact CNC machines processors to learn more about issues to which you paid attention.
