LEDs are becoming trending for their low cost in energy consumption and durability. But we should acknowledge that led lights may pile up huge thermal energy, which is the reason we should make thermal management by LED heat sinks. In this blog, we will get to know the key factor that affects led light.
Working Principle of LED Lights
Before getting deep into the question, we first learn about the working principle of led lights. LEDs are made of semiconductors containing two materials divided into N-semiconductor and P-semiconductor, of which the N owns a free electron that will move to the positive and the other one is called “Vacancies” or “virtual electrons” for lacking electron inside the atom.
Once connecting the power, the negative electron-N will move to the “Vacancies” located at the positive ( recognize that as a positive electron). Then, the LED light source will be generated by electrical energy through the interaction between N and P electrons, which saves a huge amount of energy compared with incandescent lamps.
Does LED generate heat?
Due to the thermal resistance, all electronic devices will generate heat energy. But compare with the heat generated by the former, LEDs produce less heat. Let’s talk about the micro-level dimension, we should acknowledge that there is less heat that is charged in the form of photons, will store in the LED light while the most proportion of heat is discharged when the electron and “Vacancies” are combined.
The Essential Factor That Affects LED Heat Dissipation - Junction Temperatures
There are numerous factors that the LED life such as operation temperature, thermal conductivity, ambient environment, and heat sinks material, among which LED Junction Temperature is correlated with the working principle of LED.
What is the junction temperature?
The junction temperature means the highest operating temperature of the electronic component. Generally speaking, common operating temperature ranges between -40℃ and 100℃ with sound temperature ranging from 20℃ to 30℃ and higher junction temperatures within 150°C.
Factors Affecting Junction Temperature
Color of LED Lights
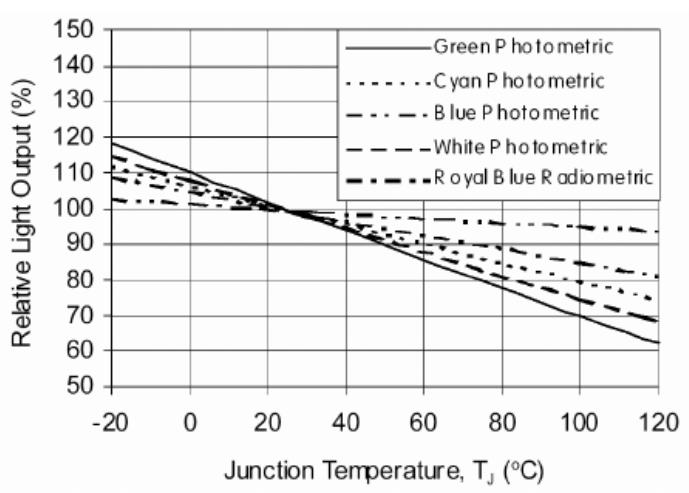
It correlates with color of the light source. Referring to the image upon, the lumen output will reduce as the temperature is rising. Looking at the image, we also recognize that there is a minimal impact to blue light with a maximal to green light, which means that you can avoid the negative impact of the LED lighting system caused by high temperature.
LED's Forward Current
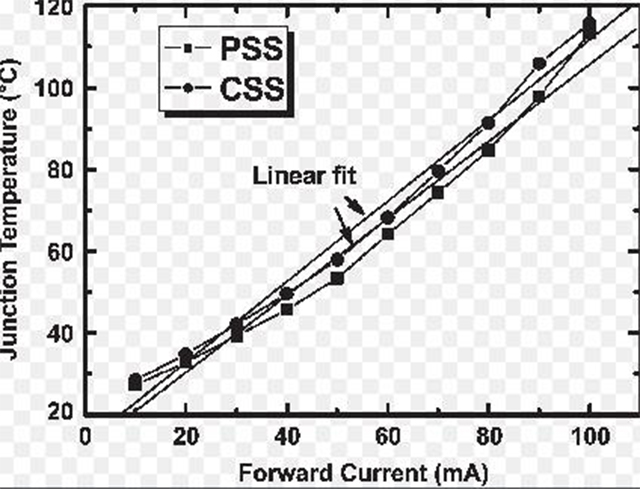
Forward current refers to current flowing to the negative from the positive In the diode. Referring to the image, Its junction temperature is correlated with forward current. Moreover, increasing temperature affects the short life of LED lighting, light output as well as low thermal resistance.
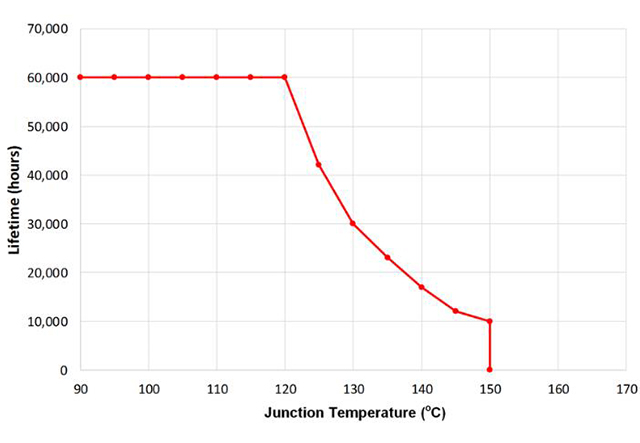
Approximately, LEDs in 25℃ can access 50,000 to 60,000 hours. Due to the high power of LED electrons, the temperature rising to 120℃ will shorten its life and reduce its lumen output with a short wavelength. Additionally, LED stays in the condition, namely “thermal runaway” when reaching 150℃, which means that exponential growth will happen unless temperatures grow rapidly.
Forward Voltage
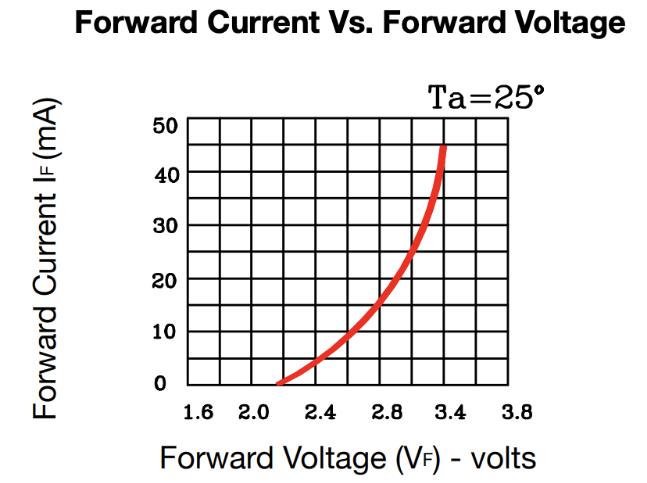
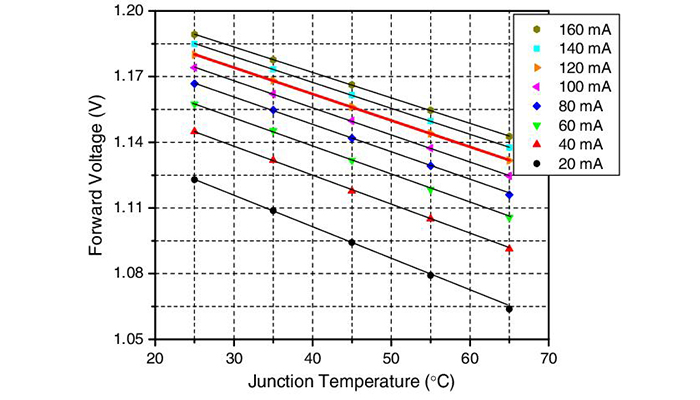
It represents a voltage connecting the positive and negative of the power. As the image mentions, the junction temperatures are rising as the voltage accrues. The reason is the junction temperatures will be reduced because of the low-power consumption where the current flowing to LED will decline by increasing the voltage.
Ambient Air Flow
Generally speaking, lower ambient temperature show a sound heat dissipation. Apart from this, you can view the LED system as a heat insulation that reaches a high temperature.
Thermal Resistance
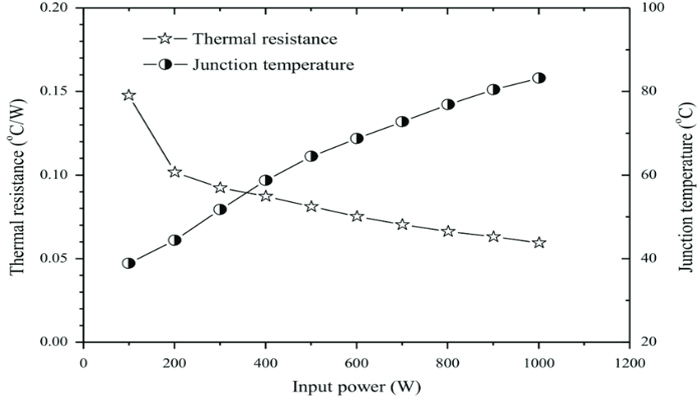
Referring to the theory, thermal resistance is correlated with voltage and output power. It can control the current flowing through the LED, illustrating that low voltage or current can avoid LEDs to produce heat.
Why You Should Choose High-Quality Aluminum Heat Sinks
The article we mentioned has illustrate how the high junction temperatures affect high power LEDs. To reach a lower temperature, you’d better to equip aluminum heat sinks for your machinery. Until now, there are 3 ways for heat transfer by using the LED heatsink with outstanding thermal conductivity: 1) Conduction( transformation into different solid substances). 2) Convection(solid to liquid such as surrounding air). 3) Radiation( heat transfer in both substances). Kaixin Aluminum is pleasant to customize heat sinks as requires.
Vapor chamber heat sinks

Vapor chamber heat sinks enjoy a very thermal management in that the aluminum alloys are thermally conductive. Given that heat flow to a low temperature from the high one, you can put your heat sinks on the heat source to get this done. It’s worth noting that Kaixin Aluminum has run a design – hollow out the interior to fill with coolant, so as to cool the LED by absorbing the heat and vaporization when heat flows across the heat sink surface.
LED extrusion aluminum heat sinks
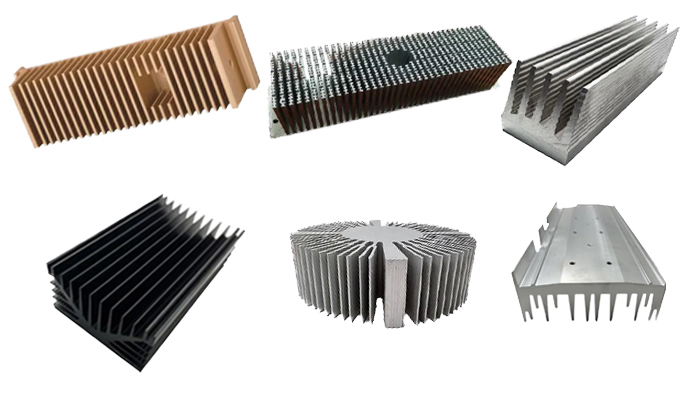

The extrusion aluminum heat sink features a simple manufacturing process for installation, therefore you can install the heat sink in the PCB. The extrusion aluminum heat sink has many fins that can add more area for heat dissipation. Kaixin Aluminum is committed to providing customized aluminum LED heat sink for our customers around the world.
Thermal Conduction Tube
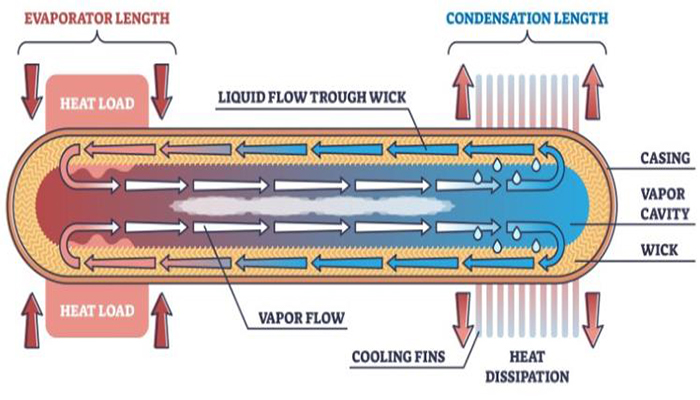
Featuring a hollow structure, the thermal tube can dissipate heat to the other material by embedding it in other materials with a well-adjusted thermal path. Compared with another heat sink without thermal tubes, it can enhance thermal performance dramatically. With a high cost, the heat sink is widely used in high-tech fields that require excellent heat dissipation performance such as new energy vehicle batteries, and photovoltaics.
